Develop protocols for antimicrobial usage by:
- Identifying common clinical scenarios
- Formulating protocols for first-line and alternative antimicrobial therapy for these conditions
- Considering appropriate antimicrobial dosing using an evidence-based approach
- Developing protocols for the use of protected antimicrobials and avoided antimicrobials
Tools to help you
To help you develop your protocols download our Protect Me policy templates.
These templates have been designed so you can fill them in when developing your own policies. When downloading them please ensure you open them on your computer rather than web browser before editing them.

The practice policy template will enable you to set doses and routes of administration of common antimicrobials. (note: if you open the form in a web browser you may lose some functionality).
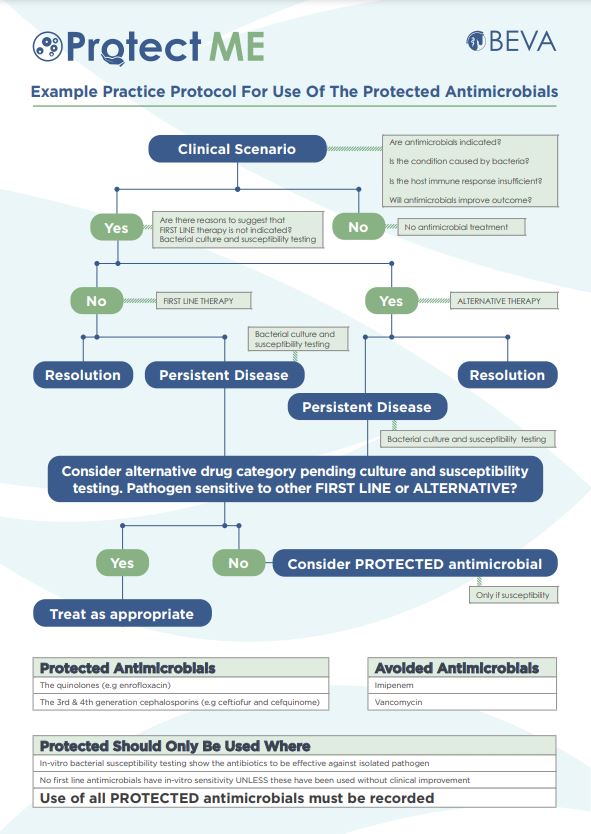
The example practical protocol will take you through the decision-making process for the use of protected antimicrobials.